How to Produce Melanin in Your Body


Melanin is a natural substance produced by the body to create pigment in skin, hair and the iris of our eyes. Additionally, melanin protects the skin from UV rays and, when sun levels rise, our dermis darkens to give us that desirable suntan. If you want to treat a skin condition or darken your skin tone for cosmetic purposes, one should note that there are no artificial method tocreating melanin in the body. The only factors which affect melanin production are genetics, an adequate intake of vitamin D and exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Keep reading here at oneHOWTO and discover how to produce melanin in the body both effectively and, more importantly, safely.
Stimulate melanin production safely
Before we can know how to produce more melanin in the body safely, we must understand what it is. Melanin determines our pigment and skin color. People with darker skin have more melanin and those with lighter skin have less. Melanin is also present in our hair and the irises in our eyes. People with albinism, for example, experience little to no pigment production, which is whyt they have very light skin, hair and eyes. The most important thing when it comes to producing melanin in the body is to, first and foremost, take care of your skin. If you have very light skin, you will need to be careful in the sun.
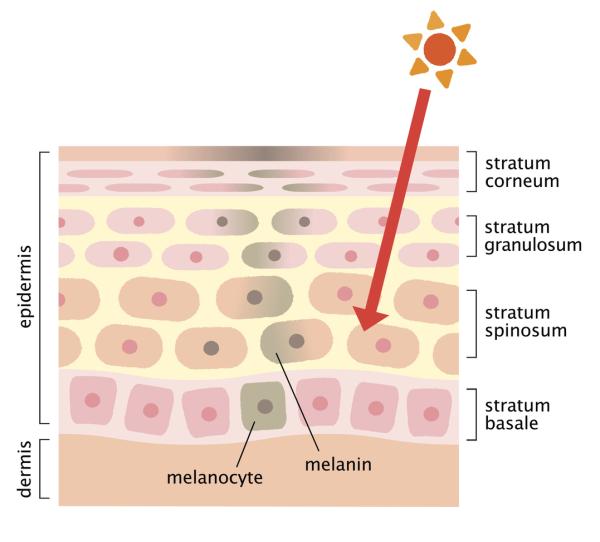
If you look at the diagram below, you will see how the melanocytes at the bottom of the epidermis produce melanin to create a darker skin pigmentation. The process by which melanin is made is called melanogenesis and the reason it exists is to protect the dermis (the lower level of skin) from harmful UV rays. UV rays come from the sun and although sunlight in small doses is good for us, especially for vitamin D production, it can also cause severe harm. Too much unprotected exposure to the sun can cause melanoma, otherwise referred to as skin cancer.
Melanin is produced to fight these UV rays. When melanin is produced, skin pigmentation darkens, but if not enough melanin is produced or you overexpose your skin to the sun, problems can arise. Melanin production in the body should, therefore, be done in a healthy way.
Wear sunscreen outside
As you now know, melanin production can be activated externally through solar exposure. So, going out in the sun to produce melanin will be effective but not necessarily safe. To do so safely, there are certain precautions you will have to take. Depending on the color or darkness of your skin pigmentation, as well as sun intensity, you will need to choose an appropriate sunblock. The appropriate sunblock is measured in SPF (Sun Protection Factor) and there are different types for different purposes; oils, creams and sprays. To get a darker tan safely, avoid the sun between 1pm and 3pm when it is at its most intense. This may seem like the best time to produce melanin, but it is also the most dangerous.
It is not just melanoma or skin cancer which you need to be worried about, but oveerexposure to the sun can also cause unsightly skin blemishes and premature skin-ageing. Additionally, many believe that you only need to take care of your skin in summer, which is not the case. UV rays can also get through clouds on overcast days, therefore, you will also have to take care of your skin during winter.

Produce melanin with beta-barotene (ß-carotene)
While it is not scientifically clear whether vitamin A helps to produce melanin in the skin, it is known to help promote healthy skin cells by enabling them to mature and function properly. In this way, it can aid melanin production and also strengthen the skin, thereby potentially reducing the harmful impact of the sun. Beta-carotene is a precursor to vitamin A and it also aids in increasing skin pigmentation. Again, it won't technically produce melanin in the skin, but it will help make skin pigmentation healthier and warmer.
Studies have shown that eating vegetables makes can visibly improve skin condition and overall skin health. Taking beta-carotene, either through supplements or beta-carotene rich foods such as carrots, pumpkins, spinach, papayas, tomatoes, red peppers and melons, can help keep your skin healthy. This will, in turn, make it easier for you to get a sun-tan and sustain it.
For more, we recommend reading our article where we discuss how to tan your skin naturally.

How to produce melanin in the skin with antioxidant-rich food
All foods rich in vitamin E either stimulate or aid in the production of melanin. Additionally, these foods are full of antioxidants and are effective when it comes to getting rid of free radicals in your dermis, thereby preventing skin-ageing. Free radicals are a normal part of most cellular processes in the body. However, over-production can cause detrimental effects, including cancer. This is why antioxidants and eating foods rich in antioxidants are key in controlling free radical production in the body.
Foods rich in antioxidants include vegetable oils (wheat oil, sunflower oil, soy, olive ...), green leaf vegetables, nuts (almonds, pine nuts, cashew nuts...), egg yolk and fruits like kiwi, mango, avocado, plums and grapes. Using vitamin E directly on the skin can also be very beneficial in melanin production or skin protection.

How can I produce more melanin with vitamin-rich food
Additional and essential vitamins which can help to stabilize melanin production in the body include vitamins B and D, which will both offer your skin protection against UV rays. Vitamin B can be found in dairy products, green vegetables, pulses, eggs, chicken and Brewer's yeast. Blue fish are also a great source of vitamin D. Healthy fatty acids like omega-3 are also incredibly beneficial. If you’re suffering from an omega-3 deficiency, we recommend eating more fish and nuts high in omega-3.
We suggest taking a look at our article where we list which foods increase melanin production.

Supplements for melanin in body
You can also resort to adding the aforementioned vitamins in the form of melanin supplements or melanin pills to your diet. L-Tyrosine and gingko biloba, are also great options when it comes to increasing the levels of melanin in your body.
You should, however, always consult a doctor before taking any type of supplement or melanin pills. There have been some studies, for example, that show that beta-carotene consumption for smoker can increase the risk of lung cancer.
Creams to put melanin back into skin
The cosmetic industry has created many creams and lotions that can help activate and produce melanin in skin. These creams often contain vitamin supplements which aim to get more melanin in your skin. They also can help maintain moisture which keeps skin healthy.
It’s important to note that not all of these products work, therefore, you should always check consumer guides beforehand. We recommendation consulting a dermatologist before purchasing any cream for your skin. A dermatologist will be able to recommend the most appropriate treatment for your skin type.

Melanin deficiency
Producing melanin will make your skin darker, but you need to be careful of both how you do it and what to do once you have it. People with darker skin are likely to develop vitamin D deficiencies if they are in areas with a lack of sunlight. People with lighter skin are naturally only able to produce a certain amount of melanin, therefore, pushing your body beyond these natural capabilities can be damaging. As always, if you are unsure of which course of action to take or are concerned about skin conditions, seek advice from a physician.
If you want to read similar articles to How to Produce Melanin in Your Body, we recommend you visit our Beauty & Personal Care category.
Tips
- Use a sunless tanner that contains dihydroxyacetone (DHA) to help you achieve a darker skin tone without sun exposure. These products only temporarily affects the outermost layer of the skin and do not change the content of melanin in skin cells.












